Complementarity: (x, y, r) feasible and xj rj =0, "j implies optimality. Then we may say that (x, y, r) is optimal if and only if x ³ 0, r ³ 0, and F (x, y, r) = 0, where F is as follows and X = diag(x), R =diag (r).
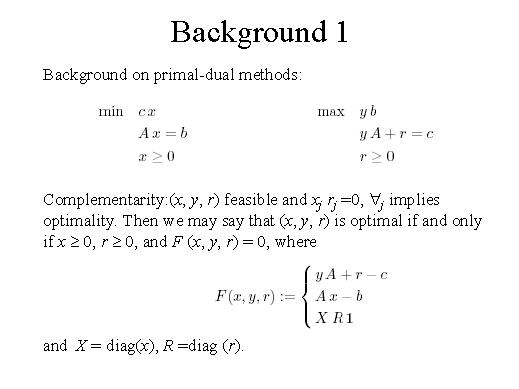
| Background
on primal-dual methods is given here. Complementarity: (x, y, r) feasible and xj rj =0, "j implies optimality. Then we may say that (x, y, r) is optimal if and only if x ³ 0, r ³ 0, and F (x, y, r) = 0, where F is as follows and X = diag(x), R =diag (r). | 
|