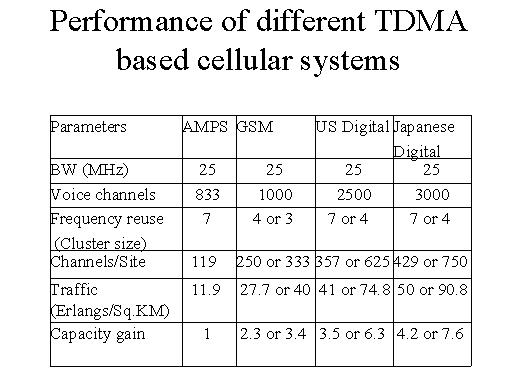
I will be considering primarily the time division multiple access systems, that is the European system, which is GSM, which is very popular, which has large penetration, the US digital and the Japanese digital. These are three time division multiple access systems.
In order to find a common base of comparison, I am taking the analogue AMPS system as well. And, again for the sake of simplicity I am considering that all of them have got equal bandwidths, spectrum bandwidths, namely 25 MHz. And thus you find now that the AMPS system support 833 voice channels only, the GSM supports 1.000, US digital support 2.500, and Japanese digital supports 3.000. And that is the advantage of the technology.
The frequency reuse, that is the cluster size, the MS has 7, whereas GSM could have either 4 or 3, US digital could have 7 or 4, to make it compatible with the AMPS, and Japanese digital also has either 7 or 4. The channels per side, therefore, you divide by the number of cluster size, therefore it becomes 119 in the AMPS, but it becomes either 250 or 333 in GSM, depending on 4 or 3 being the cluster size; with the US digital number of channels per side becomes either 357 or 625. The digital system has more, namely 429 or 750 channels per side.
The traffic capacity similarly is increasing in the various digital systems AMPS have only 7.9 Erlangs per square kilometre, whereas the GSM supports 27.7 to 40 Erlangs and US digital has 41 or 74.8 Erlangs. The Japanese systems gives you 50 or 90.8 Erlangs
Well, considering this the capacity gain, taking this as the standard there is no capacity gain in 1, but there is a capacity gain of 2.3 or 3.4 in the GSM. The US digital gives a larger capacity gain 3.5 or 6.3 and the Japanese digital system gives you the highest capacity gain for the TDMA system namely 4.2 or 7.6.
I think you have now got a fairly good idea of the various multiple access techniques used in digital and analogue cellular systems. You know that the multiple access techniques and you appreciate that the multiple access techniques play a vital role in making the cellular mobile communication systems possible as they are, because they give you the support, the large number of users which could have communication even though the bandwidth is very limited.