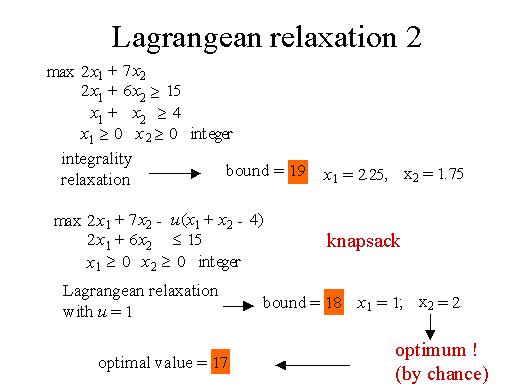
For instance, suppose we have this little problem with two constraints. The integrality relaxation provides a bound of 19. If we use the Lagrangean relaxation we drop one constraint and put it in the objection function. This turns out to be a knapsack problem which we know how to solve. The Lagrangean relaxation with u=1 provides a bound of 18. Its integral solution has value 17, which is by chance in this case just the optimum. If we compare the optimum value of the problem which is 17 with the two bounds, the Lagrangean bound and the integrality relaxation bound we see that the Lagrangean bound in this case is better. So in some cases the Lagrangean relaxation can provide better lower bounds.