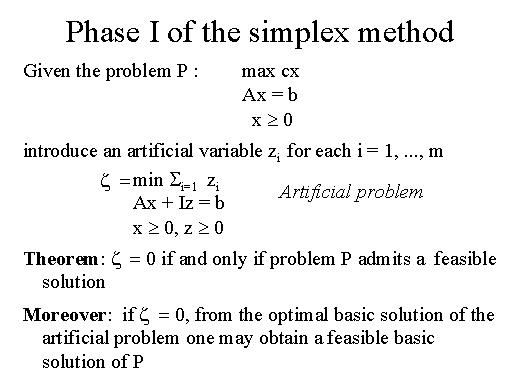
In order to complete the description of the simplex method, it remain
to show how to find an initial feasible basic solution.
This step may be performed in the so called Phase I by solving a new linear
programming problem called artificial problem. This is obtained from the
original one by introducing one auxiliary variable for each constraint
and has the form reported here. We note that since we may assume without
loss of generality that the rhs vector b is non negative, a feasible basic
solution of the artificial problem is immediately available since we can
choose the identity matrix as an initial basic matrix. Moreover it is
not difficult to see that the original problem admits feasible solutions
if and only if the optimal value of the artificial problem is 0. In this
case from the optimal basic solution of the artificial problem we get
an initial feasible basic solution for the original problem.