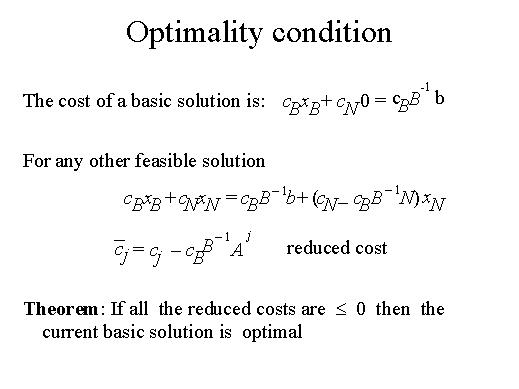
Let's now look at the generic iteration of the simplex method in which
we assume that a current basic solution is given. The first question is.
Is the current solution optimal? Optimality conditions may be stated in
terms of the so called reduced costs, which expression for each variable
is given in the formula. It is easy to verify that th objective value
of any feasible solution is equal to the value of the current basic solution
plus the sum of the non basic variables, each multiplied by the corresponding
reduced cost.
What follows is that if we are solving a maximization problem and all
the reduced costs are non positive, then the current solution is optimal.
In this case the methods ends.