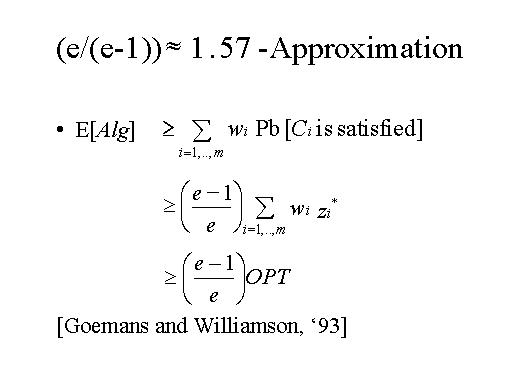
| This allows to relate the expected value of the algorithm, the expected sum of the weights of the clauses that are satisfied to the optimal solution of the fractional relaxation, that is the sum over all the clauses of w(i)z*(i) that of course is bigger than the optimal solution since this is a relaxation to the optimal solution. In this way we are able to give an improved approximate ratio 1.75 for the Max weighted sat problem, better than the very simple algorithm that assigns every variable to 1 with probability one-half and to zero with probability one-half. | 
|