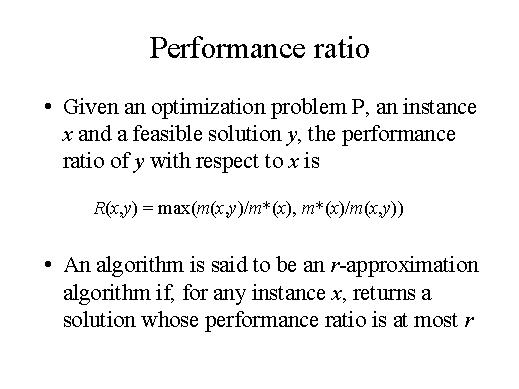
The performance ratio is the maximum between the measure of the computer solution and the optimal solution, or the measure of the optimal solution and the measure of the computer solution.
Actually this seems a slightly complicated formula, but in this way we do not have to distinguish between maximisation problems and optimization problems. In both cases in fact the performance ratio will be a number greater than 1, and as closer is this number to 1 as better is the quality of the solution computed by our algorithm.
So, we ca say that an r-approximation algorithm is said to be an r-approximation algorithm if, for any instance y, return a solution whose performance ratio is bounded by r. Where r is a given constant.