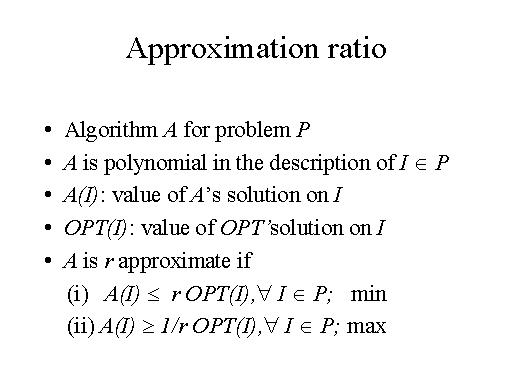
We say that the algorithm A is r approximated if for any possible instance of the problem, the solution given by A is at most r times the optimal solution for instance I. This is for minimisation problem.
On the other hand, if we deal with a maximisation problem, our algorithm is said to be r approximated if for every instance I of the maximisation problem we get a benefit that is at least a fraction r of the optimal solution.